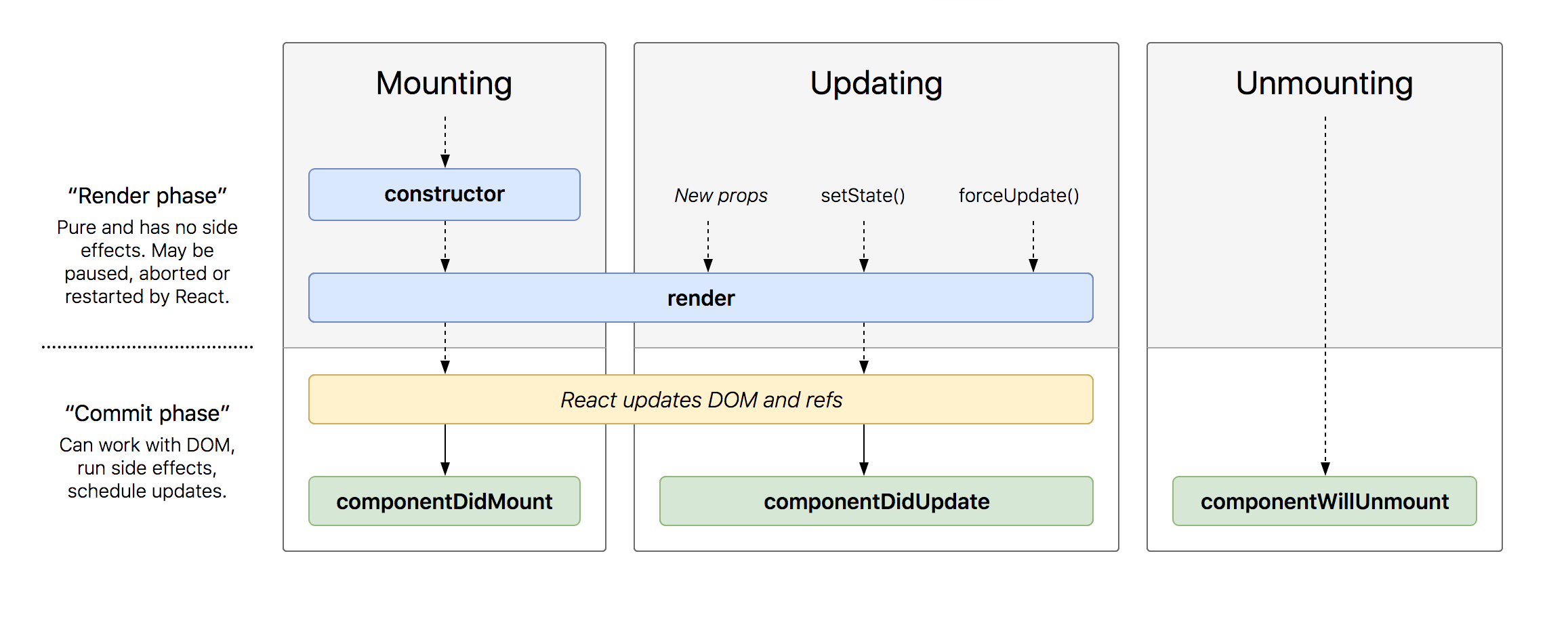
Lifecycle Diagram
There is a very useful package called create-react-app which will automatically install all your required dependencies, and set up a directory for your react app automatically.
npm install -g creat-react-app
npx create-react-app app-name
This will create a directory for the front end of your app called app-name. Inside that there will be a package.json file with all the scripts you need to create a react app, run it locally, and build a production version of that site.
The directory (app-name in this example) is automatically set up as a git repository
There are two main parts of the create-react-app directory
src folderpublic folderIf you create a production build with
npm run buildyou will additionally have abuildfolder. More on that when we talk about serving React projects next week!
src folderThe src folder is where the meat of your React project lives
App.js file lays out the whole pageindex.js draws the content to the pagepublic folderThe public folder is where your react component gets drawn to.
index.html
Let's create our first React Component! If you haven't already installed create-react-app go ahead and do that now npm install -g create-react-app
cd into your code folderfirst-reapp
h1 with the text "Hello, React!"Note: After you open VSCode it will ask if you want to use eslint from node modules. React has it's own eslint extension to properly highlight react components so use it.
By default create-react-app will set you up with a functional component.
Functional components are just functions that return JSX
But React still needs to be in scope for a functional component to work, even theough it's not explicitly used in the component
Class based components are an older way of setting up React Components, and are more representative of the way react actually works.
They are slightly less readable, and as of React 16.8 are less common since Hooks allow functional components to have all the same functionality.
This transition from class based to functional components happened very quickly not too long ago so a lot of documentation still uses class based components.
Every React component keeps track of its own state in an internal object named state. In a class based component you can access state through this.state. In a functional component you have to use Hooks to access state.
React likes to be in complete control of the page so it's important to only update the page through state, and never through direct DOM manipulation!
This is very important, and bears repeating.
Never directly manipulate the DOM when using React. All changes should be made through the state of the component using this.setState if it's a class based component, or the useState hook if it's a functional component.
Direct manipulation of the DOM will confuse React, and cause bugs.
Class based components also have direct access to a component's lifecycle methods. These are methods which get called at certain points during the component's life.
The most common of these are:
componentDidMount fires when the component is first loaded onto the pagecomponentDidUpdate fires whenever props or state are updatedcomponentWillUnmount fires right before the component is removed from the page
/