Setup
- Download MongoDB Community Server
This should include MongoDB Compass.
Compass is a GUI, or graphical user interface, that simply provides a platform to view your data without the initial need for knowing MongoDB query syntax.
This makes it a great place to start!
MongoDB Overview
- document database (NoSQL)
- horizontal sharding => can theoretically serve trillions of records
- uses JavaScript for data definition and manipulation
- built-in map-reduce for dynamic collections
- indexing on fields by value or free-text search
"Mongo is not a toy, although it can be fun to play with." - Josh Burke
Lab: Exploring with Compass
This is MongoDb's GUI tool. Let's open it up and see what it can do!
- Open Compass and click on the green "Connect" button; it defaults to
localhostfor ease of use.
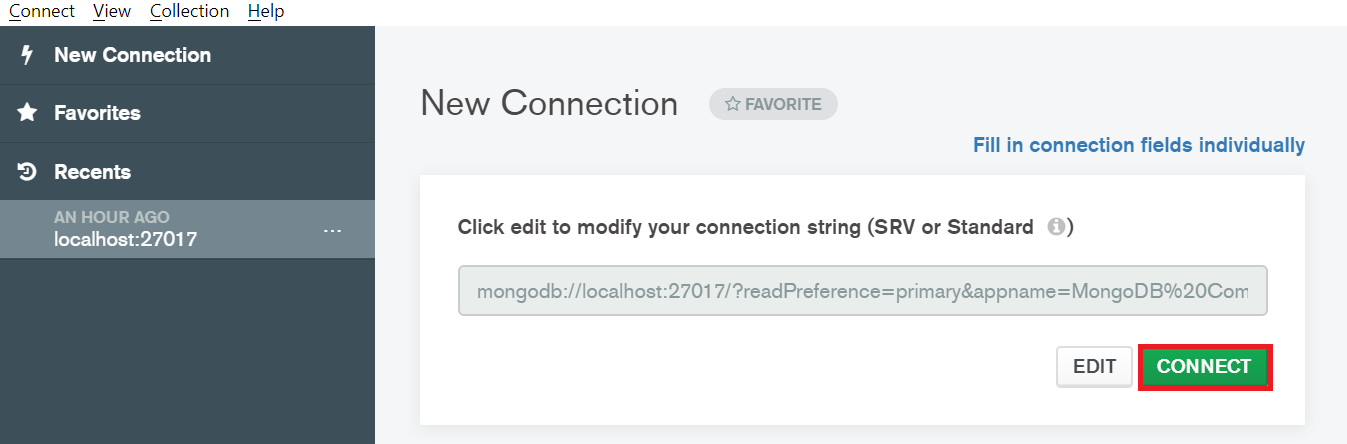
- Look for the database named
test**in the left side nav bar, and open it - Create a new collection
- In the collection you just created try running through all the CRUD functions
- Add some documents, update them, delete them...
** test is a default database name provided by MongoDB.
Concept: Database
to connect to a database you need a Mongo URI (or URL) identifying the server, port, etc.:
Connection URL format:
mongodb://username:password@host/database
for example
mongodb://mydatabasehost.com:27017/example_db
or (locally)
mongodb://localhost:27017/example_db
If no database with the provided name is given, it will default to test.
Note that the term "database" is overloaded: it refers to either:
- a single MongoDB process hosting many data sets
- a single MongoDB data set containing many related collections
Concept: Collection
A collection holds documents.
Many collections can live in a database.
This is analogous to a table in SQL.
Concept: Document
In MongoDB, a document is essentially a single JavaScript object
Like in a relational database, a document can be created, read, updated, deleted, indexed, searched for, ...
Unlike in a relational database, a document can contain any value for its fields, including arrays and nested objects.
This nesting and type-flexibility makes it very appropriate to store whatever JavaScript objects your app uses, without needing to devise a mapping between nested objects and joined relational tables.
Drivers
- MongoDB has its own query syntax that, while very similar to JavaScript at times, has its own rules and structure!
This allows MongoDB to be used with a number of languages through the use of drivers, which are language-specific! For our case, we'll be using MongoDB's Node.js driver, because we're JavaScript people, and we're working server side.
Lab: Do it with JavaScript!
Let's make our first Mongo collection!
We will insert a document into a collection that lives in a database.
Start by making new directory, and initializing it as an npm repository and installing the mongodb drivers.
mkdir mongo_example
cd mongo_example
npm init -y
npm install mongodb
Do it with JavaScript! cont.
Next, create a file called mongoClient.js
This is where we'll configure the client, or the software that connects to the server
The server, in this case, is localhost:27017
in mongoClient.js, add:
const { MongoClient } = require("mongodb");
const uri = "mongodb://localhost:27017" //mongodb connects to port 27017 by default
const client = new MongoClient(uri)
Do it with JavaScript! cont.
Now, connect to the database library, and insert a document into the books collection
Let's do this with an asynchronous function so we can harness the await keyword and keep things in order
like so:
async function run() {
await client.connect()
const database = client.db('library')
const collection = database.collection('books')
await collection.insertOne({ title: "Eloquent Javascript", author: "Marijn Haverbeke" })
await client.close()
}
run()
Note: This is a bare-bones example that does nothing for error handling. It is simply meant to demonstrate the most basic data flow.
View it in Compass
Select the database and collection on the side and...
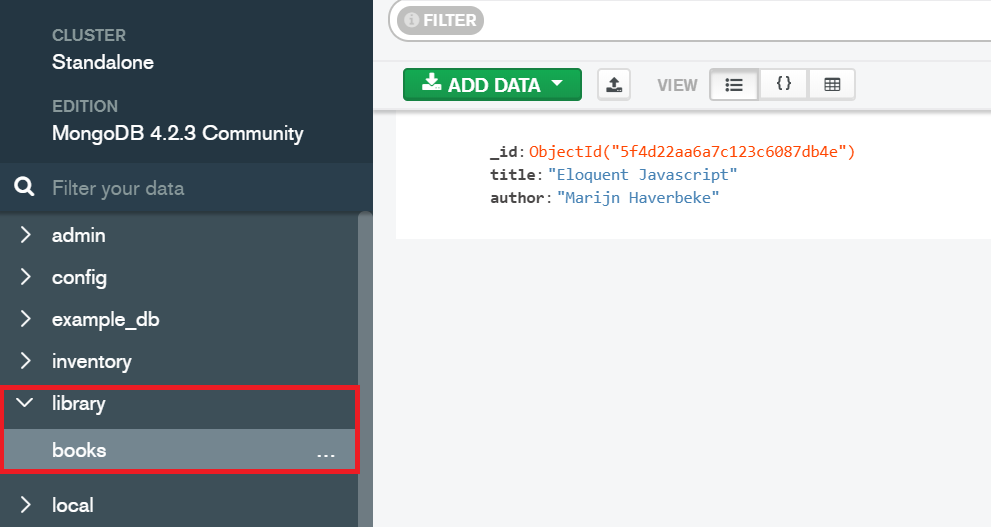
Voila! But what's that _id thing?
Concept: ObjectId
-
_idis assigned by Mongo when a document is inserted -
ObjectIdis a factory function that either generates a new id, or transforms a given string into a Mongo ID object
Links
- mongoose - mongodb object modeling for node.js