Github Forks and Clones
Git clones and forks are two different ways of creating a copy of a directory.
Cloning a repository will create a local copy of the repository that maintains a link to the remote repository.
Forking a repository creates a new remote repository in your github account that is identical to the original repository.
Cloning a Repository
To clone a repository you go to that repository on github, look for the big green button that says "Clone or download"  If you've set up your ssh key choose "clone with ssh" otherwise use "clone with https"
If you've set up your ssh key choose "clone with ssh" otherwise use "clone with https"
Copy the link it gives you to your clipboard, then in the location you want to clone your directory into type into the terminal git clone and paste the link you just copied after the git clone seperated by a space.
Cloned Repository Workflow
To make sure your local repository is up to date with the remote repository you should first pull the code from your remote repository by typing git pull into the command line
Then you can freely make changes to your code, and add and commit those changes locally. Once all your changes are committed if you type git status in the command line you should get a message that says Your branch is ahead of origin/master by N commits. This means you are good to push your code with git push
But what if there are multiple people working on the same remote repository?
Avoiding Merge Conflicts
If multiple people are collaborating on a project, they will probably share a remote repository with individual local repositories that share a single origin.
It is a very bad idea to have everyone woring on the same branch at the same time as you will get lots of merge conflicts, code will go missing or be corrupted, and everyone will by frustrated and unhappy.
The solution to this is to create a new branch git checkout -b unique-branch-name add and commit to this branch, then push the branch to your remote repository git push origin unique-branch-name. When you're ready to bring your new features into the master branch you can open a new pull request to compare your branch with master (or any other branch), resolve any merge conflicts,and merge it in.
Pull Requests
Creating a pull request is fairly simple you just need to navigate to the "pull" tab 
Select the branches you want to compare (usually master and your working branch) 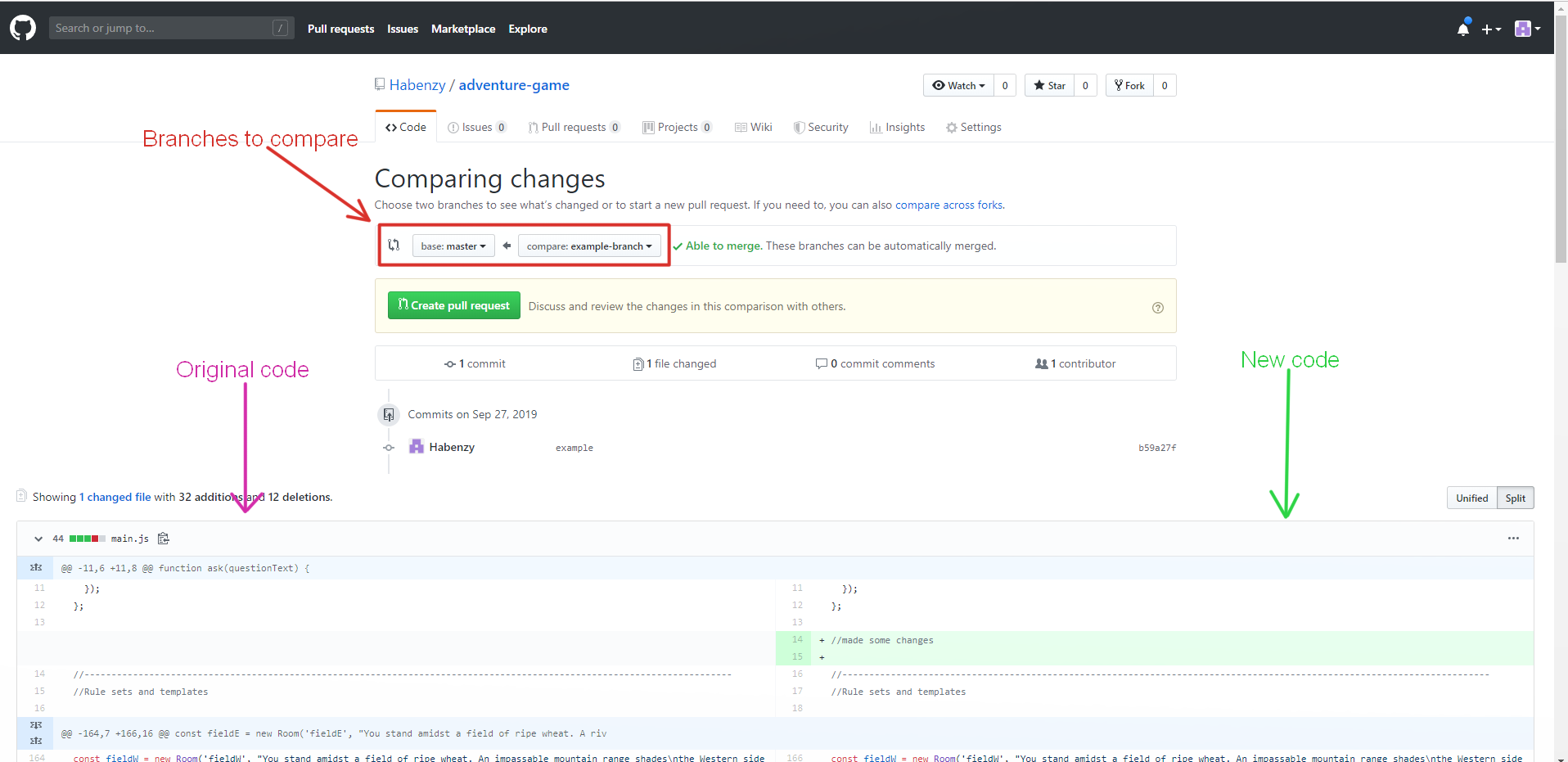
Then click on "Create pull request"
You can now ask your teammates to review yor pull requests, and they can add comments right on your code for any suggested edits or potential bugs.
Forking a respository is creating a duplicate of that repo on github.
To add code to a forked repository, you create a new branch on the fork of the upstream repo. After coding and committing locally, you will first pull changes from upstream down. Once the upstream changes are integrated into your local work, you can push your branch up to the fork. Lastly, a PR is created to merge the branch from the fork into a branch from the original or origin repo.
 If you've set up your ssh key choose "clone with ssh" otherwise use "clone with https"
If you've set up your ssh key choose "clone with ssh" otherwise use "clone with https"
